Proposals invited on clean meat tech
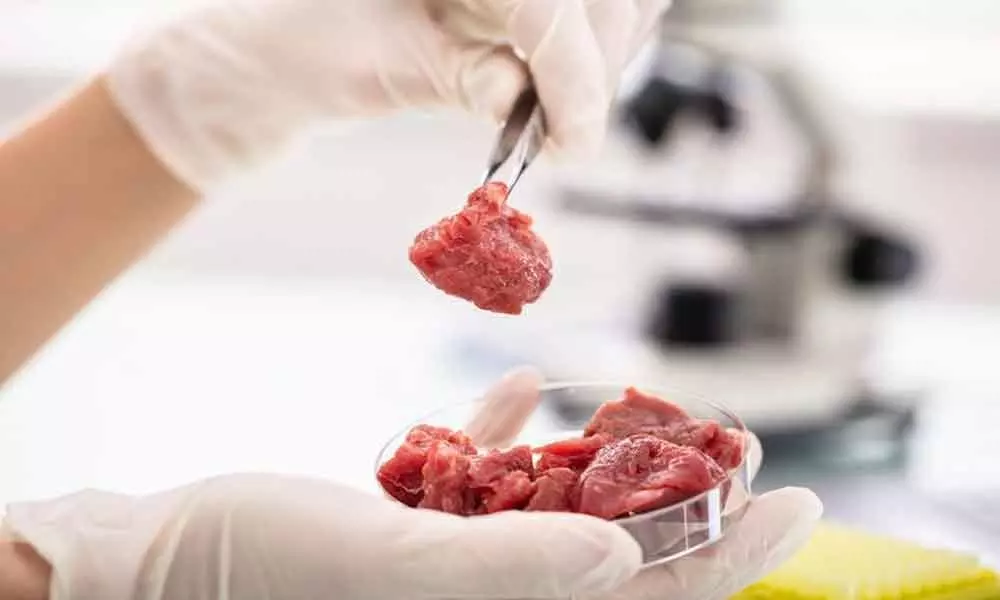
Hyderabad: In a joint effort to support the advancement of scientific research on clean meat in India, the Atal Incubation Centre at CCMB Centre for Cellular and Molecular Biology here, Humane Society International/India and the Good Food Institute India, have launched an innovation challenge to advance development and production of meat grown by culturing animal cells.
The three organisations are calling for proposals from entrepreneurs and the scientific communities to publish review papers on technologies that will help accelerate the development and scale-up of clean meat (also called cultivated meat or cell-based meat) in India.
Open to scientists from both private and public institutions, the grant will be provided to four selected proposals. Each review should examine the state of science in a specific area of clean meat, offer concrete recommendations for scale-up, and be accepted for open-access publication in high-visibility, peer-reviewed journal.
Alokparna Sengupta, managing director of Humane Society International/India, said, "This call for proposals is an exciting opportunity to tap into the vast technical talent and expertise India possesses. We are confident this project will bring out novel research that can serve as a base for further scientific innovation in the Indian clean meat sector."
Varun Deshpande, managing director for Good Food Institute India, said, "Cell-based meat has immense potential to create a reliable, affordable supply of protein for the world's population, and to align human and planetary health. India's talent pool and business environment are hugely important to this future, and we look forward to stimulating further Indian activity in the sector through this Innovation Challenge."
Clean meat is being hailed for its potential to provide the world's growing population with sustainable protein. Instead of raising and slaughtering animals for meat, clean meat is genuine animal meat, cultivated from cells outside of an animal. It can replicate the sensory and nutritional profile of conventionally produced meat and is comprised of the same cell types and arranged in the same 3D structure as animal tissue.


