Live
- Sai Durgha Tej gets special gift
- They always want me to win, and now I feel lucky to have been offered a story like ‘Zebra’: Satyadev Kancharana
- ‘Democracy first, humanity first’: PM Modi in Guyana's parliament on two countries' similarities
- PKL Season 11: Telugu Titans register third straight win to top standings
- Is Pollution Contributing to Your COPD?
- NASA Unveils Underwater Robots for Exploring Jupiter's Moons
- Additional Central forces arrive in violence-hit Manipur
- AR Rahman and Saira Banu’s Divorce: Legal Insights into Common Issues in Bollywood Marriages
- 82.7 pc work completed in HPCL Rajasthan Refinery area: official
- Curfew relaxation extended in 5 Manipur districts on Friday
Just In
2023 was one of the best years for emerging stock markets other than China

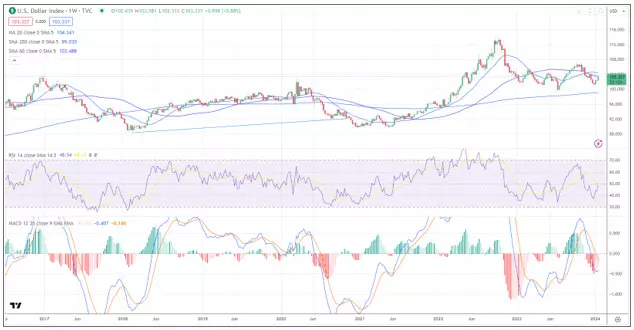
Emergy market equities rebounded in 2023 after experiencing a downdraft in 2022. Despite a 10% rally in the MSCI EM Index in 2023, the index failed to...
Emergy market equities rebounded in 2023 after experiencing a downdraft in 2022. Despite a 10% rally in the MSCI EM Index in 2023, the index failed to recover most of the losses the index experienced in 2022. China was one of
the biggest detractors of the performance of Emerging Market equity indices in 2023. Blackrocks iShares ETF that tacks E.M., excluding China, gained 17% in 2023. The MSCI China index declined approximately 13% in 2023, the
third consecutive year of declines.
Why Did China's Stock Market Underperform
While many of the E.M. equity markets outperformed, the Chinese markets underperformed. Several issues led investors to shun the Chinese markets. Consumer spending was meager, and youth unemployment accelerated
higher. Additionally, China started experiencing a real estate issue as borrowing became too expensive.
China's economic growth has significantly affected its stock market performance. A slowdown in the Chinese economy can negatively impact corporate earnings and investor sentiment, leading to underperformance of the stock
market.
Changes in government regulations or policies can significantly impact the Chinese stock market. For example, stricter regulations on specific industries, changes in foreign investment policies, or crackdowns on fraudulent or
speculative activities can create uncertainty and dampen investor confidence, resulting in underperformance.
Concerns over financial stability or risks within China's financial system can also impact the stock market performance. Issues like excessive debt levels, non-performing loans in the banking sector, or potential asset bubbles can
create uncertainty and lead to underperformance.
Market sentiments and investor psychology play integral roles in stock market performance. Fear, uncertainty, or negative sentiment can influence investor behavior and lead to selling pressure, causing the market to underperform.
Additionally, sluggish demand capped consumer prices during 2023, creating the risk of deflation.
What is Deflation?
Deflation refers to a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services within an economy. It is the opposite of inflation. In a deflationary environment, the purchasing power of money increases over time as
prices decline.
Prices of goods and services across various sectors decline over an extended period. Deflation can be widespread or concentrated in specific industries or regions.
Deflation often results from decreased aggregate demand, which can be caused by factors such as a weak economy, high unemployment, or reduced consumer spending. As consumers anticipate further price declines, they may
delay purchases, decreasing overall expenditure.
Deflationary conditions can discourage business investment and expansion as companies experience reduced revenue and profitability. Firms may delay capital expenditures, reduce production, or cut costs, including laying off
employees.
Deflation can increase the debt burden on borrowers. As prices decline, the real value of debt rises, making it more challenging for individuals and businesses to repay loans. This situation can further dampen spending and
economic activity.
The performance of the global market can impact the Chinese stock market. Factors like changes in global interest rates, market volatility, or economic conditions in other major economies can affect investor sentiment toward
Chinese stocks and result in underperformance.
While moderate deflation may have some positive effects, such as increased purchasing power, severe and prolonged deflation can have detrimental economic consequences. It can reduce production, investment, and
employment, creating a negative cycle of falling demand and economic contraction.
Are EM Equities Correlated to U.S. Markets?
The positive returns experienced in E.M. markets ex-China are likely due to the robust returns seen in the U.S. equity markets. Historically, EM markets have performed well when the U.S. equity markets are rising. E.M. markets
are usually also negatively correlated to the movements in the U.S. dollar. As the dollar declines in value, E.M. markets generally outperform.
Correlation is a statistical measure that quantifies the relationship between two variables. It indicates how closely and in what direction two variables move together. The coefficient ranges from -100% to +100%.
A correlation coefficient of +100% reflects a positive correlation. A correlation coefficient of -100% indicates a negative correlation,.
A correlation coefficient of 0 indicates no observable relationship. In other words, there is no consistent pattern or trend in the relationship between the variables.
It's important to note that correlation measures the strength and direction of the linear relationship between variables but does not imply causation. Just because two variables are positively or negatively correlated does not
necessarily mean that one variable causes the other to change.
A weaker dollar can potentially benefit emerging market equities. A weaker dollar relative to other currencies can make exports from emerging markets more competitive. As the dollar's value declines, goods and services priced in
other currencies become relatively cheaper for international buyers. This situation can boost demand for emerging market exports, increasing revenues and potentially benefiting companies listed on the stock market.
A weaker dollar can make emerging market assets, including equities, more attractive to foreign investors. When the dollar depreciates, investors holding other currencies can purchase more shares or have increased purchasing
power in these markets. This scenario can increase capital inflows, increasing equity prices in emerging markets.
Many emerging markets are rich in natural resources and are major commodity exporters. Commodities such as oil, metals, or agricultural products are often quoted in dollars. A weaker dollar can result in higher dollar-
denominated commodity prices, positively impacting the revenue and profitability of commodity-producing companies in emerging markets potentially benefiting their stock prices.
Some emerging market countries have significant levels of external debt denominated in U.S. dollars. A weaker dollar can reduce the burden of servicing this debt as it becomes less expensive in domestic currency. This situation
can improve the financial conditions of governments and corporations, potentially benefiting their stock prices.
Why Did the Dollar Decline?
After peaking in 2022, the dollar moved lower in 2023, which helped E.M. markets gain a toe hold (chart). The dollar started to move lower as bond market participants started to price in the potential for the Federal Reserve to
cease interest rate hikes, shift gears, and reduce borrowing rates.
Interest rates can have a significant impact on the value of a currency, including the dollar. Higher interest rates tend to attract foreign investors looking for better investment returns. When interest rates in the United States rise,
foreign investors often move capital into the country to take advantage of higher yields. This increased demand for the dollar can strengthen its value relative to other currencies.
Interest rate differentials between countries can impact currency exchange rates. If the interest rates in the United States are higher than those in other countries, it can increase demand for the dollar in foreign exchange markets.
Traders seeking to benefit from the interest rate differential may buy the dollar and sell other currencies, driving up the dollar's value. The reserve is also true. When interest rates in the United States are beginning to fall, there can
be a decline in the dollar's value.
Changes in interest rates by the Federal Reserve (the central bank of the United States) can influence the dollar's value. When the Federal Reserve raises interest rates, it signals tightening monetary policy, making the dollar more
attractive to foreign investors and potentially strengthening its value.
Lower interest rates are often used to combat decelerating growth. When interest rates fall, borrowing becomes less expensive, which can increase overall spending and help control declining employment. If the Federal Reserve
reduces interest rates, it can signal a weaker dollar.
How Do Emergy Market Equities React to Lower U.S. Interest Rates?
Lower U.S. interest rates can make investing in emerging market equities more attractive than U.S. investments. This situation may lead to increased capital flows from global investors seeking higher returns in these markets,
potentially driving up the prices of emerging market equities.
Lower U.S. interest rates could weaken the U.S. dollar, which may result in the appreciation of currencies in emerging markets. A stronger local currency can benefit emerging market equities, reducing import costs and boosting
export competitiveness.
Lower U.S. interest rates may signal a more accommodative global monetary policy, which could improve market sentiment and increase risk appetite among investors. This positive sentiment may contribute to a rise in emerging
market equity prices.
The Bottom Line
What seems clear is that most E.M. equity markets in China continue to rally along with the United States equity markets. Built-in the U.S. equity markets are declining U.S. interest rates, which could continue to weigh on the dollar
and buoy equity markets in the United States and Emergy Markets Ex-China. China continues to be mired in a slump as consumer sentiment and spending have yet to rebound. In the United States, which has helped buoy many
E.M. equity markets, a soft landing seems to be in the cards, as inflation has eased and labor markets remain robust.
Disclaimer: The information provided in this article is for general informational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for professional advice and should not be relied upon as such. The author and the website make no
representations or warranties of any kind, express or implied, about the completeness, accuracy, reliability, suitability, or availability of the information contained in the article. Any reliance you place on such information is therefore
strictly at your own risk. The article may contain links to external websites for additional information, but the author and the website do not endorse or guarantee the accuracy of content on those sites.

© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com






