Indian researchers develop 'organoid' to help in neurodegenerative diseases
Share :
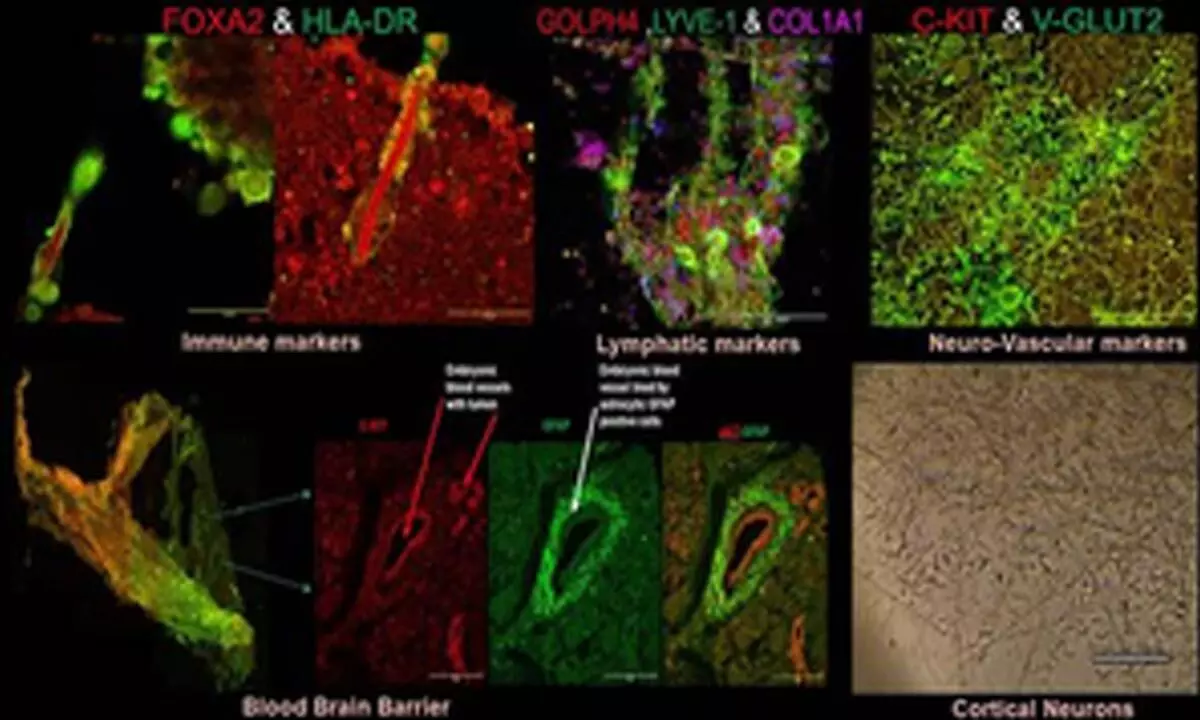
A team of researchers at the PGIMER on Thursday said they have developed a new prototype to generate neurovascular tissues/organoids from "autologous" blood (your own blood) that can help in precision medicine.
New Delhi: A team of researchers at the PGIMER on Thursday said they have developed a new prototype to generate neurovascular tissues/organoids from "autologous" blood (your own blood) that can help in precision medicine.
The prototype can help develop patient-specific embryoid models (called precision medicine) for congenital neuro-sensory, neuro-developmental and neuro-degenerative diseases like autism, ADHD, ANSD, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson's.
It can also be used for deciphering genetics and neural circuits, testing drugs bypassing the blood-brain barrier, and identifying novel biomarkers for early neurological diseases, said researchers from Post Graduate Institute of Medical Education & Research (PGIMER).
The research, funded by Anusandhan National Research Foundation (ANRF/erstwhile SERB) can produce "functional vascularised embryoids on its own and requires no guided patterning".
It is cost-efficient as it requires no specific differential media, growth factor or differentiating morphogens for culturing, but only "autologous" plasma and blood cells.
The field of neural organoids is rapidly progressing and has fueled the hope for improved understanding of brain development and functions, modelling of neural diseases, discovery of new drugs, and supply of surrogate sources of transplantation.
"The implications are vast for studying neurological (neuro-sensory/motor and neuro-immune) disease pathways, neuro-regeneration, pre-clinical neuro-imaging, and endogenous gene editing, and autologous immunotherapies for tumours, and auto-immune diseases," said researchers.
The researchers said they are in the process of filing a patent for the prototype at the Punjab State Council for Science and Technology, Chandigarh. They are employing these models to understand the genetic basis of neuro-sensory hearing loss and auditory comprehension challenges (altered central auditory activity) in children with congenital Sensorineural Hearing Loss (SNHL) (early onset).













