Overview of Digital Dental Technologies
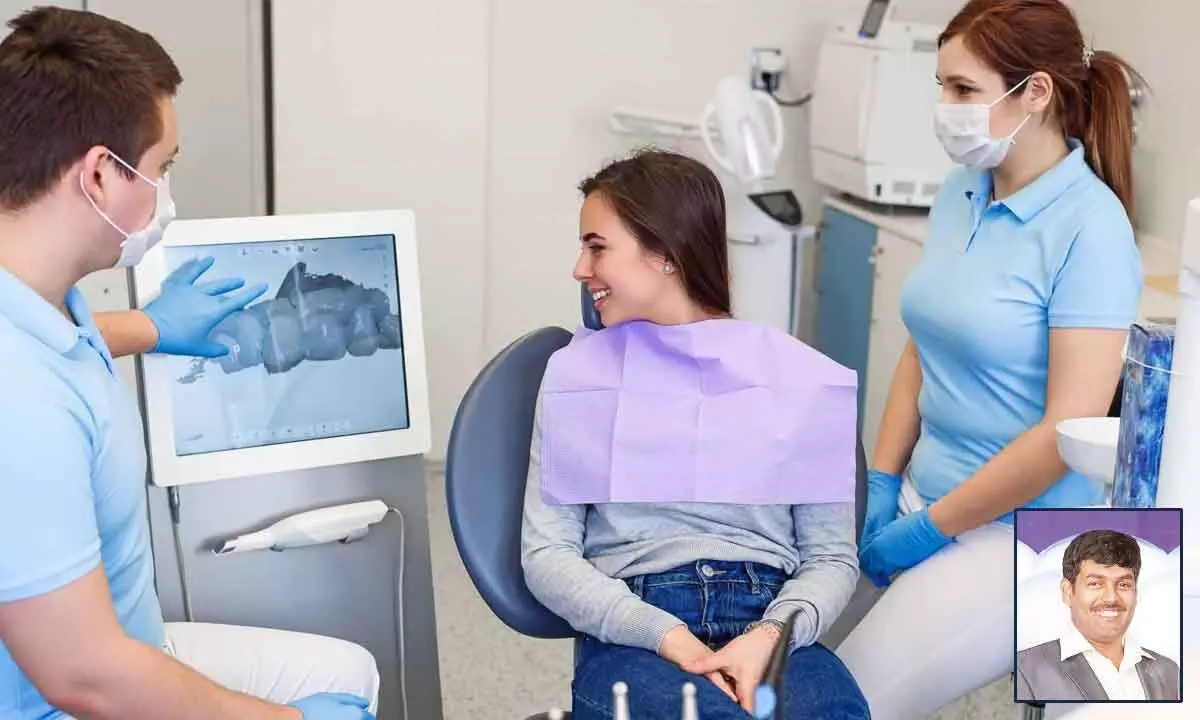
Dr Naveen Kumar T, BDS, Certified BPS Dentist, Switzerland talks about the digital dentistry uses and dental technologies or devices that incorporates digital or computer-controlled components to carry out dental procedures rather than using mechanical or electrical tools
Digital dentistry uses dental technologies or devices that incorporates digital or computer-controlled components to carry out dental procedures rather than using mechanical or electrical tools. This is used both for restorative and diagnostic purposes. Digital solutions allow dentists to take impressions quicker and give patients the option to get treatment in a single visit thus speeding up processes.
Intra oral cameras
X rays show only 2D images, whereas Intra-oral cameras show 3D surfaces of the tooth Examples include specific locations and sizes of cavities, cracked teeth, excessive erosion, abrasion and many more.
Conventional dental impressions made from dental arches give negative imprints y gives a positive imprint on to a computer screen, spectrophotometer helps in getting exactly the matching colour of the teeth to implants.
Intra oral 3D scanner simplify the complex procedure of taking dental impression, providing accurate scanning result and clearer teeth structure information to the dentist within just 2 minutes. These impression
Digital X-rays
Digital radiographs capture dental images through a sensor that processes the image onto a computer screen. Digital X-rays provide greater comfort than traditional X-rays and reduce radiation exposure Additionally, digital radiographs allow dentists to magnify images for greater diagnostic accuracy, ensuring more timely and appropriate treatments.
Diagnodent is a tool used for the early detection of cavities. This technology uses sound pulse and laser to detect caries earlier than traditional methods so that treatment can commence immediately, limiting the amount of dental decay. Thus preserving maximum amount of healthy tooth structure
TekScan (T-Scan)
A computer that uses an ultra-thin electronic sensor to digitally evaluate a patient’s bite relationships. The Wand is a computerised tool that can deliver anaesthesia in a slow and methodic manner thus making injections painless
Dental Lasers -these are precision tools for many gingival procedures causing less bleeding and trauma to surrounding areas.
The digital approach extends to the fabrication of dental restorations as well. Computer-Aided Design (CAD) and Computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) systems allow for the creation of highly precise dental crowns, bridges, and dentures. This helps to customise restorations according to the patient’s unique dental anatomy, leading to better aesthetics and improved functionality.
Dentists can now simulate treatment outcomes using digital smile design software, giving patients a preview of their post-treatment appearance. This helps in setting realistic expectations and enhances patient engagement by involving them in the treatment planning process.
Moreover, digital dentistry has streamlined record-keeping and communication within dental practices. Electronic Health Records (HER) ensure seamless access to patient information, treatment history, and diagnostic images. This facilitates collaboration among dental teams.
One of the cornerstones of digital dentistry is the use of 3D imaging and scanning technologies. Computed Tomography (CBCT) scans, providing dentists with intricate 3D images of the oral and maxillofacial regions. This technology aids in accurate diagnosis and treatment planning, particularly for complex cases such as dental implants, orthodontics, and oral surgeries. With CBCT, dentists can visualise bone density, nerve pathways, and overall anatomy, ensuring safer and more effective treatments.
([email protected], 988521060, 8125087234 and 040 24020601.








