Live
- Indian students' concerns about employment, safety, and visas discourage them from applying to UK universities
- Candlelight Concerts Makes a Dazzling Debut in Hyderabad with Sold-Out 'Tribute to Coldplay' Show
- Shubman Gill Sustains Thumb Injury Ahead of Perth Test; Devdutt Padikkal Joins Test Squad
- Unlock Loot Boxes, Diamonds, Skins, and More Exciting Rewards with Garena Free Fire Max Redeem Codes for November 16
- Regarding the DOGE Plan, Vivek Ramaswamy stated, "Elon Musk and I Will Take a Chainsaw to Bureaucracy"
- Sudanese army says repulsed paramilitary forces attack in western Sudan, killing over 80
- Jaipur Open 2024: Baisoya makes a grand comeback to clinch title in marathon playoff against Rashid Khan
- Jamaat-e-Islami Hind President asks cadre to reach out to larger society beyond community
- Why PM mum on Caste Census, removing 50 pc quota limit: Rahul Gandhi
- Barrackpore Municipality Vice-Chairman found dead at home, suicide note suggests blackmail
Just In
x
Highlights
Marketing management can be defined as the analysis, planning, implementation and control of activities designed to create, develop and maintain mutually beneficial relationships with the customers to achieve organisational objectives. The activities mentioned above can be explained using the 4Ps frame work. First introduced in 1960 by Jerome McCarthy and later popularised by marketing Guru Philip Kotler, 4Ps can be used as the building blocks to understand marketing.
Half of the money I spend on advertising is wasted and the problem is I don’t know which half” Lord Leverhulme; “The Real question is, will they buy it?” Noel Peebles; “Nobody counts the number of ads you run, they just remember the impression you make” Bill Bernbach. These famous quotes reflect the paradox of product promotions – to do or not to do.
Marketing management can be defined as the analysis, planning, implementation and control of activities designed to create, develop and maintain mutually beneficial relationships with the customers to achieve organisational objectives. The activities mentioned above can be explained using the 4Ps frame work. First introduced in 1960 by Jerome McCarthy and later popularised by marketing Guru Philip Kotler, 4Ps can be used as the building blocks to understand marketing.
4Ps are referred to as marketing mix. The four Ps are the Product (that satisfies the need). The price or the exchange value that has to be given to procure the product, promotion or the information or the knowledge that is needed by the customer to evaluate; access and procure the product and finally distribution or the placement of the product into the hands of the customer.
The 4Ps concept predominantly looks at marketing from the producer’s view point. 4Ps can also be explained by looking at it as 4Cs, which is looking at the 4Ps from the customer’s side. In the 4C frame work, product becomes the means to customer need satisfaction, price becomes the cost the customer has to pay, promotion becomes the communication by the company and placement becomes convenience.
Marketing communication process: The third P or the promotion is the communication of the company to the customer. The communication process starts with the sender or the company that desires to communicate about its offerings to the target audience, its customer, and consumer/client base.
The company encodes (converts information or an instruction into a particular form) the message and puts it into a promotional media or a channel. The customer receives the message, decodes (convert a coded message into intelligible language) and gives feedback. In marketing the feedback takes the form of positive feelings about the product, positive word of mouth, and positive associations or in many cases propels the customer to buy the product.
Objectives of marketing communication: It can be explained by using the AIDA model. AIDA stands for attention, interest, desire and action. The marketing promotion of the company should first grab the attention of the receiver. Then it should create interest, this part is very critical. If the receiver is passive then the entire promotional campaign is wasted.
The interest should further be deepened to the next level where the customer feels that he or she needs to have the product and without that product there is a disapproval from others and mental discomfort or disturbance. This disturbance can be lessened or eliminated by the next step, action which is procuring the product.
Hierarchy of effects model: A model that explains the promotional objectives even better is the hierarchy of effects model that incorporates two more elements to the AIDA model. This model has six elements, i.e., awareness, knowledge, liking, preference, conviction and finally purchase. The receiver is cycled through awareness which knows that the product exists, then knowledge of what the product is and how to use it, then liking the product.
Liking is then elevated to preference and finally conviction. Conviction is a state where the potential customer prefers the brand over others and finally this would lead to purchase. To put it in a nut shell promotion objectives start with creating interest, persuading and inspiring customers which leads to increase in demand, sales, product differentiation and increased product loyalty. In the cluttered market place promotion is also used to remind and assure the customers that their buying choice is a wise and a justified decision.
Traditional elements of the promotional mix: The traditional elements of promotional mix include advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, public relations/publicity and direct marketing. Advertising: It is a paid form of non-personal communication. One of the most popular forms of mass promotions, it is a method of communicating with a huge customer base instantly.
Types of advertising include print advertising (newspapers), magazines and journals; electronic broadcast media advertising that is television, radio, and cable. Finally advertising can be carried out using OOH (Out of House) advertising that is hoardings, transit media, wall paintings etc.
Sales promotion: It is the short-term inducement given to the customer to visit the point of purchase (POP) and procure the product as fast as possible. It aims to trigger shot term sales. The problem with advertising is that it says “buy” but many ignore the message and postpone the purchase. Sales promotion provides the incentive or motivation to purchase, so it says “buy now.”
Promotions that target the final customer are called sales promotion and include price offs, discounts, one plus one, premiums, free samples, gifts etc. Promotions that target the marketing middlemen or the intermediaries are called trade promotion and include price display allowance, quantity discounts, merchandising assistance, incentives on target completion etc.
Personal selling: It involves person to person interaction between the buyer and the seller.The seller with personal interaction finds out the needs of the customer and satisfies it with suitable product. Often the most effective method of promotion it allows immediate feedback and satisfaction but it is expensive.
Public relations: It is the paid form of non-personal communication where the sponsor or the company is silent. Public relations is the activity where the company is involved in fostering positive interactions with the public that it encounters including customers, the general public, the suppliers, the middlemen and the government. It includes conducting press conferences, sending out press notes and giving information about the products and the organisation, handling rumours, and negative publicity.
Direct marketing: It is the direct interaction between the buyer and the seller without any channel. Often the most cost effective direct marketing methods include direct selling, direct response marketing, telemarketing, database marketing, sky television and home shopping. It includes the concept of catalogue marketing which has been taken over by online shopping.
Problem with traditional methods of Promotion: In the bygone days there was TINA factor. There was no choice. The customer could very easily be targeted by carefully chosen media and there was an assurance that he/she could be contacted effectively and as often as possible. But things have changed now and there is an explosion of the media vehicles and many new forms of entertainment have come up.
There is a division of the interest; costs have gone up dramatically and attention spans have reduced. All this has resulted in less attention spans and increased cost of promotions and definite dilution of the promotional efforts. There is lot of duplications and many of the elements of the promotion mix are at logger heads with each other. There are tuff wars and this leads to lot of bad blood with each element trying to outwit the other at the cost of overall promotional effectiveness.
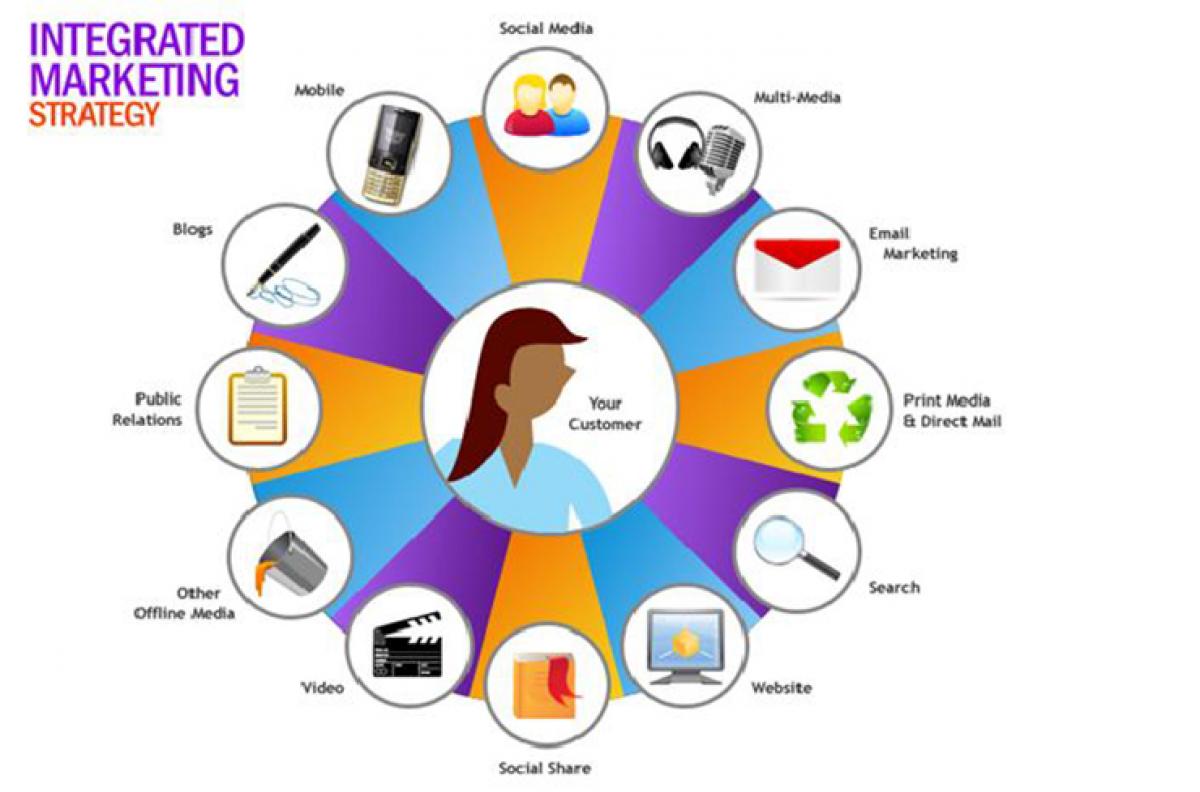
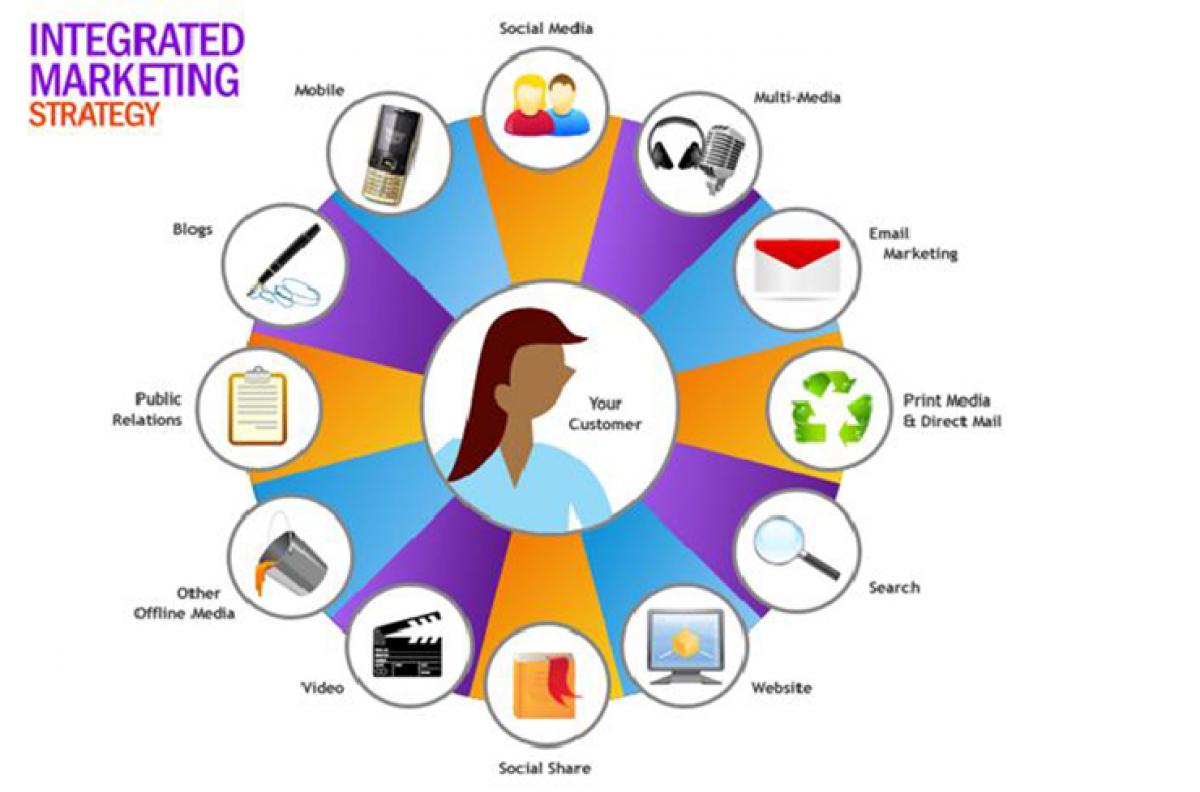
Integrated Marketing Communication: It is the coordination of all the promotional elements, advertising, sales promotion, personal selling, public relations, direct marketing and online marketing/social media with each other and with other 3Ps of marketing, so that all elements talk with the same voice, talk the same message and talk with the same emphasis.
The key features of IMC: Any IMC programme should start with the customer. In the cluttered market place no opportunity should be lost to engage the customer as many times and as frequently as possible. To achieve this any form of relevant contact or touch points have to be used. All the promotional elements should talk with a single voice, single message, single emphasis and single focus. IMC should strive to build long term relationships that foster positive feelings and loyalty. Finally IMC should affect behaviour and develop hard core loyalty.
IMC at work: A new brand of biscuit commercials are shown on the television, the same product’s advertisements are advertised in the newspapers at a price-off offer, the company sales people do door to door selling, and huge outdoor hoardings can be seen in the city. The company releases press release and holds a press conference where it extols the school children to do social activities and distributes free t-shirts with the brand of the biscuits prominently visible.
When the customer goes online he/she finds banner advertisements of the biscuit. The customer is invited to like the company’s official homepage. On visiting the Facebook page the customer is redirected to the company’s website. Thus the customer is seamlessly moved from one media to another and he/she is continuously exposed to the same message.
Advantages of IMC: The Company is totally focused on the customer and satisfying the customers’ needs. Substantial cost can be saved as all promotions are coordinated and there is no duplication of promotional efforts. IMC lead to inter departmental integration as all the marketing departments have to work together.
There will be synergies and everyone in the company now works towards achieving the same objectives. All the external arms like advertising agencies, market research agencies, PR outfits, event management companies will be trained to talk the same message, same voice and with the same emphasis.
It looks as if the company is spending a lot but the company actually spends a lot less but as the activities are coordinated there is big bang for the promotional budget. Brands and companies will be more noticed. Seamlessly the customers can be made to notice the promotion, called stickiness the message tends to stick to the psyche of the consumers.
Through careful tracking and monitoring, companies can find out which promotional elements are delivering results and which are not. IMC forces the companies to cut the flab and be trim and try to save cost by looking at non-traditional methods of promotions like digital marketing (E-commerce) and at social media platforms.
By:DR M ANIL RAMESH

Next Story
More Stories
ADVERTISEMENT
© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com







