Environmental issues in India Biodiversity
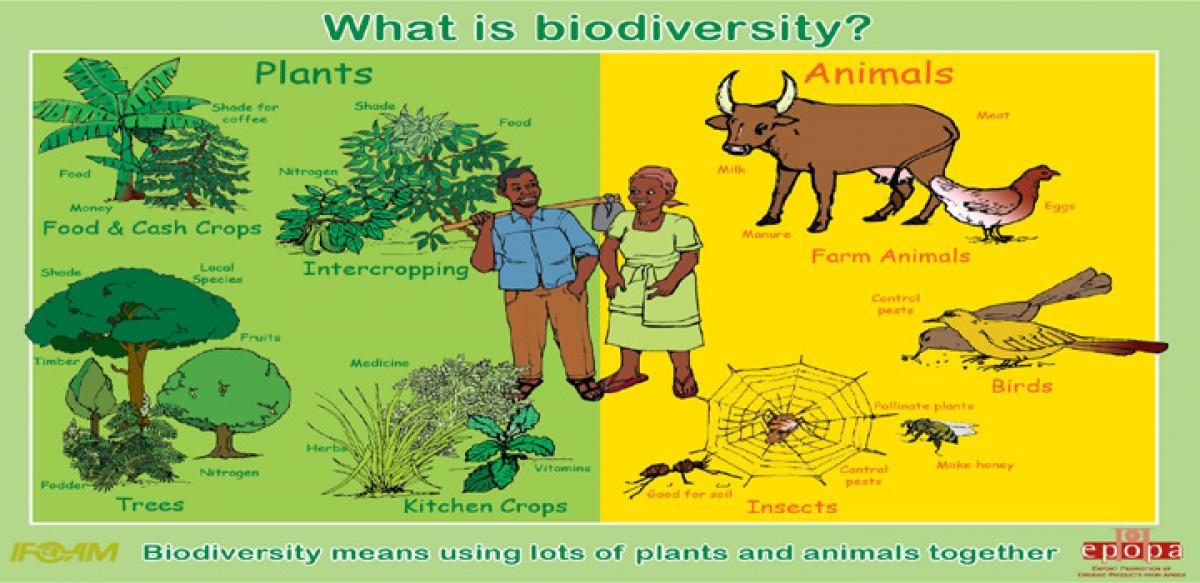
Biodiversity is a term given to the variety of life on Earth. It is the variety within and between all species of plants, animals and micro-organisms and the ecosystems within which they live and interact. In simple terms the land, air and sea are home to the minutest insects and the largest animals, which comprise a huge variety of interconnecting and interdependent forces, this is bio diversity.
Biodiversity is a term given to the variety of life on Earth. It is the variety within and between all species of plants, animals and micro-organisms and the ecosystems within which they live and interact. In simple terms the land, air and sea are home to the minutest insects and the largest animals, which comprise a huge variety of interconnecting and interdependent forces, this is bio diversity.
India is immensely rich in biodiversity; it has 7-8% of recorded species of the world. It ranks seventh in mammals, ninth in birds and fifth in reptiles in terms of species richness. Its position is tenth in birds with 69 species, fifth in reptiles with 156 species and seventh in amphibians with 110 species. Its share of crops is 44% as compared to the world average of 11%. It also has 23.39% of its geographical area under forest and tree cover. Of the 34 globally identified biodiversity hotspots, India harbors 3 hotspots.
Biodiversity in India is important because among many other things it provides food from crops, livestock, forestry and fish. It is of use to modern agriculture as a source of new crops, as a source material for breeding improved varieties and as a source of new biodegradable pesticides. It is a rich source of substances with therapeutic properties. Several important pharmaceuticals have originated as plant-based substances, which are of incalculable value to human health.
The industrial products like timber, oils, lubricants, food flavours, industrial enzymes, cosmetics, perfumes, fragrances, dyes, etc… can all be derived from various plant species. It is a source of economical wealth for many areas, such as many parks and forests, where wild nature and animals are a source of beauty and joy, attract many visitors.
Ecotourism in particular, is a growing outdoor recreational activity. Biodiversity has also great aesthetic value. Examples of aesthetic rewards include ecotourism, bird watching, wildlife, pet keeping, gardening, etc. It is also essential for the maintenance and sustainable utilization of goods and services from ecological systems as well as from the individual species.
These services include maintenance of gaseous composition of the atmosphere, climate control by forests and oceanic systems, natural pest control, pollination of plants by insects and birds, formation and protection of soil.
But citizens and government activities in India that are motivated by development, economic, cultural and aesthetic goals are causing environmental and ecological changes of great significance. Because of such harmful human activities species go extinct and ecosystems become degraded or polluted. For example the destruction of habitats is the primary reason for the loss of biodiversity.
When People cut down trees or burn a forest the natural habitat of a species is changed or destroyed. Activities like poaching and trade in species and species’ parts also constitute a major threat. Over-fishing and widespread marine pollution and human induced climate change threaten the survival of marine biodiversity. Pollution, oil and gas drilling and oil spills may increase the risks of extinction of marine organisms.
Therefore one of the most essential environmental issues in India now is the conservation of biodiversity. Also owing to the reasons mentioned in paragraph3, biodiversity is so useful that it becomes imperative for India to look after, improve and protect it from harmful activities.
People should respect other life-forms. Both governments and citizens have no moral right to destroy nature and other beings that reside on earth. This Topic is part of Civil Services Preliminary Examination and Paper3 of General Studies syllabus