Live
- After caste census, Dalits, tribals, poor will recognise their true strength: Rahul Gandhi
- Who was Birsa Munda, whose 'Ulgulan' declared the end of British rule in Jharkhand?
- Five selected as Indian Rhodes Scholars for 2025
- Raj Thackeray releases MNS election Manifesto with a ‘key’ to implementing it
- COP29: 3 methodologies approved for issuing high-integrity carbon credits
- MP: Celebrations of Birsa Munda's birth anniversary begin in presence of Guv, CM in Shahdol
- NGT seeks details of waste to energy plants not complying with norms
- Dev Deepawali 2024: Significance, Rituals, and How to Celebrate with Lamps
- Air quality in Kolkata dips to ‘very unhealthy’ category
- Air pollution may raise risk of lung cancer, asthma in children, say experts
Just In
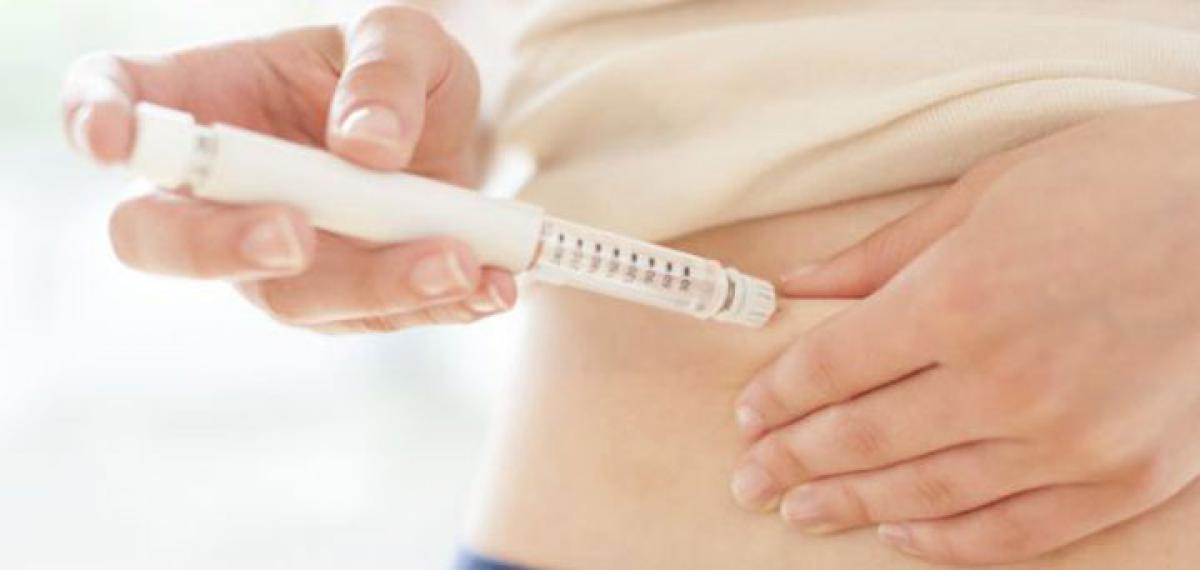
The Research Society for the Study of Diabetes in India (RSSDI) has endorsed FIT (Forum for Injection Technique) India recommendations for effective management of insulin injection technique for diabetics.

The Research Society for the Study of Diabetes in India (RSSDI) has endorsed FIT (Forum for Injection Technique) India recommendations for effective management of insulin injection technique for diabetics.
The initiative is expected to benefit over two million diabetes patients with regards to long time insulin and insulin-like therapy adherence, smooth drug delivery and minimisation of adverse side effects.
As per the FIT recommendations, special emphasis is to be given to counter complications arising out of incorrect usage of injections and usage in special groups like elderly population, pregnant women and people with weak immunity. The recommendations also suggest correct injection technique that can help protect against lipohypertrophy (lump formation), unexplained hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and blood glucose variation.
The success of insulin injection therapy and the adherence to it depends on factors, such as a smooth insulin initiation process with counselling that alleviates the fear of needles, the insulin regime, length of needle and the method of administration. Shorter needles can provide safety from injecting into muscle, as an insulin injection in the muscle may lead to hypoglycemia.
Prof S V Madhu, Professor and Head, Dept of Medicine and Endocrinology, UCMS-GTB Hospital and President, Research Society for Study of Diabetes in India (RSSDI) said, “The number of people with Type-2 diabetes is on the rise in every country, with earlier diagnosis and longer life spans meaning that there is an increasing likelihood that they will need to use injectable therapies to control their condition. Therefore, it becomes extremely important that standard insulin techniques and best practices are adopted across the country at par with global standards.”
Dr Rajeev Chawla, Senior Consultant Diabetologist and Secretary, RSSDI said, “Poor technique, including the use of an inappropriate needle length, failure to rotate injection sites and the re-use of needles, can lead to insulin being absorbed in an unpredictable manner, potentially leading to complications, such as hypoglycaemia, hyperglycaemia and even ketoacidosis in patients with Type 1 diabetes. Injection technique addresses all these factors.”
In the past, studies cited reasons as to why patients dread insulin injection usage. According to a study published in Diabet Med, 20 per cent of insulin users often or sometimes skipped their injections while 10 per cent restricted their number of daily injections due to needle anxiety, pain or embarrassment. Another study has found that bacterial contamination, local inflammatory changes and injection pain increased in direct proportion to needle re-use, highlighting an increased risk of infection.
Doctors feel that the rate of insulinisation is low in India. This is a roadblock in the optimal management of diabetes because of fear of needles and lifelong dependence on insulin. It is estimated that two thirds (64 per cent) of insulin users develop lipohypertrophy at some time in their lives that can result in varied absorption and consequent erratic glycaemic control.
Dr Laurence Hirsch, Vice President, Global Medical Affairs, Diabetes Care at BD, said, “For patients, the understanding and practice of correct injection technique has the potential to make a real difference to their lives, helping to deliver their insulin more consistently, reduce discomfort and minimise the risk of developing associated complications.”
As per a study published in Journal of Clinical and Translational Endocrinology (2014), correct injection technique education not only improved blood glucose control in people with diabetes, but also provided greater satisfaction with therapy and lowered the daily consumption of insulin after only three months; a relatively short period of time.

© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com







