How culture impacted human evolution
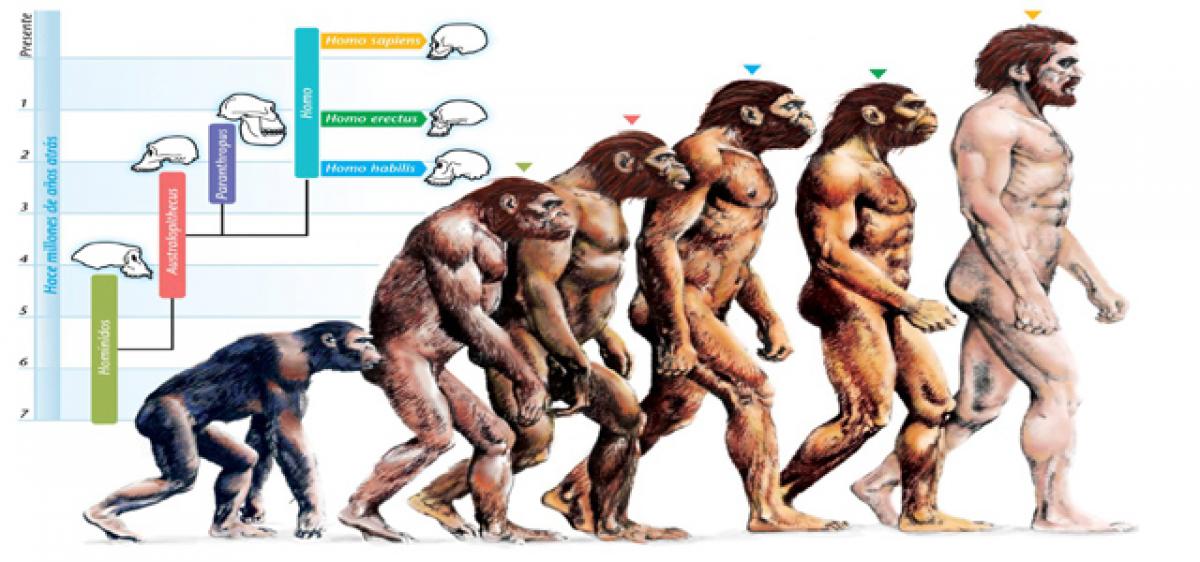
Human evolution, which has revolutionised humans from other mammals and animals, is a lengthy process. Humans originated from ape like ancestors about one to six million years ago. It is an interesting fact that both humans and chimpanzees evolved from a common ancestor yet the humans have higher intellect and adaptability compared to apes.
Human evolution, which has revolutionised humans from other mammals and animals, is a lengthy process. Humans originated from ape like ancestors about one to six million years ago. It is an interesting fact that both humans and chimpanzees evolved from a common ancestor yet the humans have higher intellect and adaptability compared to apes.
Humans are primates. Physical and genetic similarities show that the modern human species, Homo sapiens, has a very close relationship to another group of primate species, the apes.
The most important and earliest trait that distinguished humans from apes is bipedalism -the ability to walk on two legs -evolved over four million years ago. Other important human characteristics -such as a large and complex brain, the ability to make and use tools, and the capacity for language -developed more recently. Many advanced traits - including complex symbolic expression, art, and elaborate cultural diversity - emerged mainly during the past 100,000 years.
Human evolution includes interdependent yet separable process namely biological and cultural evolution. It is obvious that culture had little or no influence on the lives of the Australopithecines (the first humans).
In the beginning Australopithecines, lived in herds like animals in their environment. Evolutionary pressures which was responsible for change in other organisms has steered the human evolution too.
Once the Australopithecines, began to develop a dependence on culture for survival, it has become an important aspect and influenced the biological evolution. Sherwood L, Washburn a physical anthropologist has termed the relationship between the human biology and culture as ‘Biocultural feedback’. The interplay between biological change and cultural change led to human evolution and why humans are different from other organisms.
The genes which improved the human capacity for culture have had an adaptive advantage. The ultimate result of the interplay between the biology and culture has led to the significant acceleration of human evolution, as manifested in, among other features, the growth of our brain and its mental capacity over the past two million years.














