Live
- Sudanese army recaptures capital of Sinnar State in central Sudan
- Kishkindha Kaandam Review: Some movies prove not to compromise in having a good cinematic experience and this is one of them
- Son-rise: Hemant Soren grows taller as tribal leader, makes father proud
- ISL 2024-25: 10-man NorthEast United FC hold on to take three points vs Punjab FC
- BGT 2024-25: Jaiswal’s application, commitment to form a partnership was so impressive, says Gilchrist
- BGT 2024-25: Personally, I am very happy with my performance, says Harshit Rana
- Pakistan's Lahore remains world's most polluted city despite light drizzle
- Asha Nautiyal retains Kedarnath for BJP, to be back as MLA after 12 years
- India leads world in science, innovation research: Minister
- Flash flood in Indonesia's South Tapanuli claims two lives
Just In
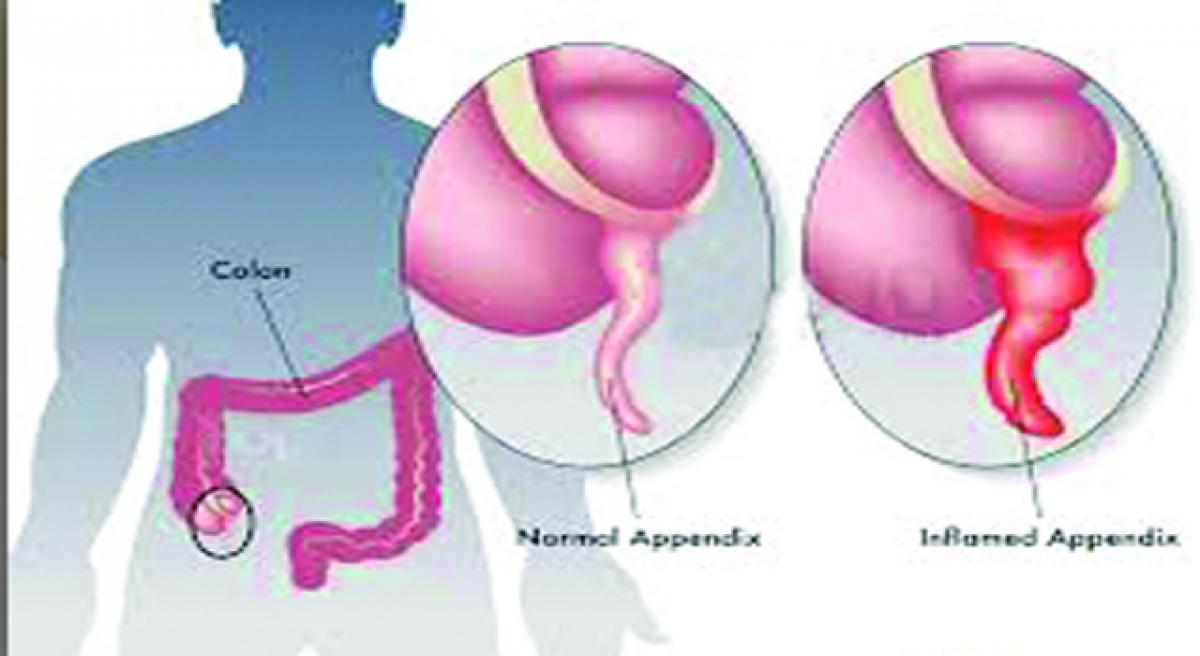
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix. It is thought that appendicitis begins when the opening from the appendix into the caecum(The cecum is a short, pouch-like region) becomes blocked. The blockage may be due to a build-up of thick mucus within the appendix or to hardened dry stool that enters the appendix from the caecum.
What is Appendicitis
Appendicitis is inflammation of the appendix. It is thought that appendicitis begins when the opening from the appendix into the caecum(The cecum is a short, pouch-like region) becomes blocked. The blockage may be due to a build-up of thick mucus within the appendix or to hardened dry stool that enters the appendix from the caecum.
What are the Symptoms of Appendicitis
The main complaint in Appendicitis is abdominal pain. The pain is at first diffuse and around the navel, but later, after a few hours it is localized to right lower abdomen in front of the right hip bone and the navel. This point is known as McBurney's point. Nausea and vomiting also occur with appendicitis.Low grade Fever sets in usually and later may become moderate to high grade if infection is not controlled.
How is appendicitis diagnosed
The Doctor diagnoses Appendicitis by taking a thorough history and by physical examination. Patients often have an elevated temperature, and there usually will be tenderness in the right lower abdomen when the doctor presses there. Sometimes when the doctor presses on the abdomen and then quickly releases his hand, the pain becomes suddenly but transiently worse known as Rebound tenderness.
A normal urinalysis is more characteristic of appendicitis and rules out Urinary disease, especially, stones in which condition urine has pus and Red Blood cells. An abdominal x-ray may detect the fecalith or sometimes dilated small bowel loops. An ultrasound examination that uses Ultrasound waves to identify organs within the body. An experienced Sonologist can identify an enlarged appendix or an abscess.
How Appendicitis is treated
Once a diagnosis of appendicitis is made, the Appendix has to be removed as early as possible. Appendicitis is removed through surgical procedure. In Open appendectomy, an incision is made inthe abdominal wall in the area of the appendix till the abdomen is opened. The surgeon then identifies the appendix, usually located in the right lower abdomen. After examining the area around the appendix to be certain that no other problem is present, the appendix is detached from caecum by severing its blood supply and attachments.
Laparoscopic Appendectomy is a newer technique for removing the appendix. The laparoscope is a thin telescope attached to a video camera which is inserted into the abdomen through a small puncture viewed on a Television or Monitor. If appendicitis is found, the appendix can be removed with special instruments that can be passed into the abdomen through small puncture.
Complications arising from Appendicitis if not addressed on time
If the patient does not consult a doctor immediately, the inflammation and infection spread through the wall of the appendix, the appendix can rupture at a weak spot after bulging. After rupture, infection can spread throughout the abdomen and lead to Peritonitis. Sometimes it is localized to a small area surrounding the appendix resulting in Abscess in right lower abdomen
Another complication of appendicitis is Intestinal obstruction. In this situation an emergency operation may be required which can be risky.
A feared complication of appendicitis is Septicemia where infecting bacteria enter the blood and travel to other parts of the body. This is a very serious, even life-threatening complication.
Conclusion
There is no one test that will diagnose appendicitis with certainty. Therefore, the approach to suspected appendicitis might include a period of observation and tests.
All cases of acute appendicitis can now be treated laparoscopically, where 3 small cuts are made to insert telescope and instruments to operate. Microlaparoscopy is a recent advancement where the port sizes are reduced to 3 and 5 mm , hence giving better cosmesis. The main advantages of this less-invasive surgery are:
- Less postoperative pain.
- Faster recovery and return to normal activity.
- Shorter hospital stay (24-36 hours, versus two to seven days).
- Fewer post-operative complications.
- Minimal incisions and scars
Dr Suresh Chandra Hari
MBBS, MS (Gen Surgery)Medical Gastroenterologist Continental Hospitals www.continentalhospitals.com 7799661661

© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com







