Live
- Basavanagudi Kadalekai Parishe: Govt gives good news to groundnut traders
- Yanamala blames YSRCP policies for collapse of state economy
- Call to inculcate habit of reading books
- 63% parents give milk to their kids to maintain intake of calcium
- Maoist Leader Manjula Surrenders in Warangal, Receives ₹20 Lakh Reward
- Kartika Purnima celebrations fervour marks Telugu States, devotees flock to shiva shrines
- YSRCP alleges meagre fund allocations for Super Six schemes
- Telangana CM Reviews Plans for First Anniversary of State Government
- Vijayawada: Kindness Day celebrated
- Rajamahendravaram: Students advised to set clear goals
Just In

x
Highlights
Agriculture plays a pivotal role in the economy of Telangana and the better performance of this sector is vital for inclusive growth. Telangana went in for the Green Revolution in rice cultivation in the 1970s. There have been significant changes in the structure and performance of the agrarian economy in the state in the recent years.
Agriculture plays a pivotal role in the economy of Telangana and the better performance of this sector is vital for inclusive growth. Telangana went in for the Green Revolution in rice cultivation in the 1970s. There have been significant changes in the structure and performance of the agrarian economy in the state in the recent years.

Telangana State is endowed with bountiful resources having good soils, diversified cropping pattern and major irrigation systems fed by rivers like Godavari and Krishna. Agriculture is a way of life, a tradition that has shaped the culture and economic life of the people of Telangana.
Therefore, it will continue to be central to all strategies for planned socio-economic development of the State. The State Government has emphasized the need to achieve 6% growth rate and increased returns on investment to farmers through improved technology, effective extension reach, efficient input delivery, mechanization, marketing tie up, adequate credit and crop insurance.
The total Geographical area of the State is 114.84 lakh ha with a Gross Cropped Area of 62.88 lakh ha in the year 2013-14.
.jpg)
Telangana is situated on the Deccan Plateau, in the central stretch of the eastern seaboard of the Indian Peninsula. In Telangana State, there are varieties of soils ranging from fertile alluvial to very poor sandy soils. Various soil types abound, including chalkas, red sandy soils, dubbas, deep red loamy soils, and very deep black cotton soils that facilitate planting mangoes, oranges and flowers, exist in Telangana. Red soils are predominant, accounting for 48 percent of the total area. Other soil types in the State are black cotton soils, alluvial, rocks and boulders accounting for 25 percent, 20 percent and 7 percent of the area, respectively. The soils in Nizamabad, Warangal and Nalgonda are deficient in nitrogen (less than 44%). Phosphorous deficiency (less than 55%) is prevalent in the districts of Adilabad, Medak, Mahabubnagar and Nizamabad.
During the 2015-16, the focus on agriculture strategies is as follows:
• Soil mapping, digitization of all villages and strengthening of soil testing labs.
• Seed production especially soybean seed production in coordination with PJTSAU and TSSDC to make the Telangana state self sufficient in soybean seed production.
• Crop production of various agricultural crops in coordination with PJTSAU.
• Re-engineering extension approach for effective extension reach.
• Empowering the farmer with advance agricultural practices.
• Capacity enhancement of Departmental Staff for an efficient extension of technology.
• Ensuring timely input supply.
• Regulation of inputs and quality control.
• Promotion of Integrated Crop Management (ICM) through INM, IPM, efficient water management, etc.
• Promotion of organic farming to meet the demand of World Market.
Agro Climatic Zones
Based on rainfall, type of soils and cropping pattern, etc., the State is divided into four Agro-climatic zones.
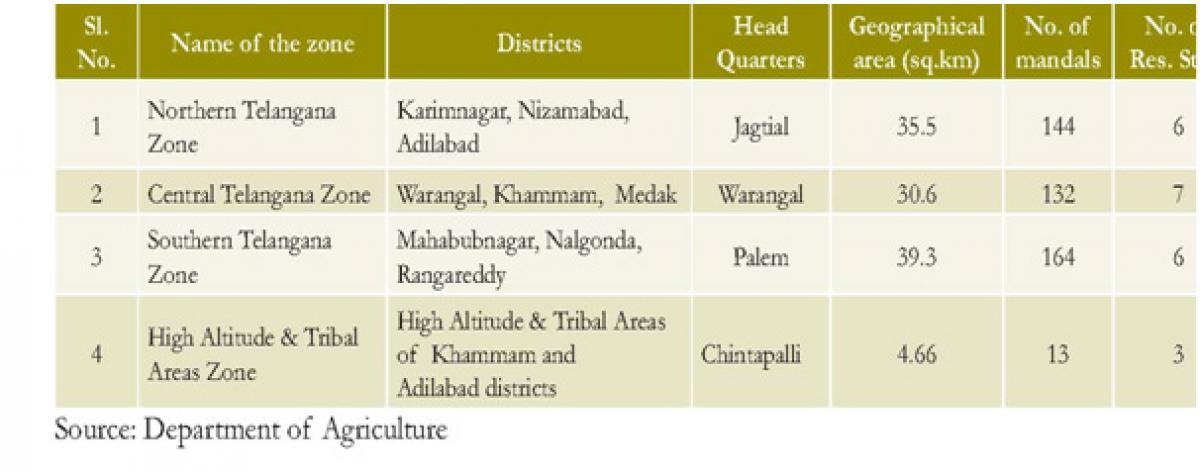
Agriculture Potential of Telangana:
• Soils of Telangana are well drained to moderately well drained and provide favorable environment for soil fertility management.
• Soils are suitable for wide range of crops including food grains, oil seeds, pulses, fruit crops, pastures, forestry etc. There are a number of agriculture-related-institutions of importance in Telangana, including ICAR Institutes viz. DRR, DOR, MANAGE, NIPHM and NAARM, NIRD, NFDB, CRIDA and NRCS.
• Food grain production recorded a growth rate of 3.97% (CAGR) as against 2.43 % at all India level.
• 37.42 lakh quintals of seeds of various crops with an area of 3.22 lakh acres, HYV Paddy, Hybrid paddy, Maize, Cotton and Bengal gram etc.,are produced.
Constraints in Telangana Agriculture
While there is lot of potential for growth in agriculture, there are constraints hampering the same . The major constraints are as follows.
• Low and erratic rainfall leaves many areas under unprecedented drought, while some areas are subjected to floods.
• Semi-arid climate restricts the growth of natural vegetation, due to which, scope of organic matter development in soils is limited and, therefore, the most soils are inherently poor in available Nitrogen, the chief nutrient for plant growth 63% of the agriculture is rainfed, which is exposed to the hostilities of climate.
• Among the farming community, about 85% of farmers are either marginal or small with poor socio¬economic condition High labour cost and low mechanization levels have increased the cost of cultivation.
Agriculture Vision
Despite the constraints, it is important to improve the agricultural situation in the state, duly harnessing the available agricultural potential and integrating it with technology and resources. Keeping in view the future requirements of agricultural production, a vision for Telangana is framed as put forth here under: Empowering the farmers in seed management, enabling them to acquiring good quality seed at the right time and at affordable cost.
• Making farming a commercially viable endeavour.
• Providing easy access to inputs, finance, technology and IT.
• Increasing irrigated area by utilizing the available surface and groundwater potential.
• Providing means for land development for efficient soil and water management.
• Providing trained extension staff for technology transfer at the door step of farmers.
• Identifying the yield gaps and bridging them through suitable technologies.
• Motivating for the farmers to adopt Integrated Nutrient Management (INM) and balanced fertilization with necessary demonstration and training support.
• Providing short term weather forecasting for instant action.
• Promoting farm mechanization through access to farm machinery and equipment at affordable cost.
• Strengthening IT to help the farmer in accessing information on weather, input availability and markets.
• Improving water use efficiency through drip and sprinkler irrigation.
• Empowering the farmers for eco-friendly agriculture through INM and IPM.
• New Initiatives for Sustainable Agriculture Developm3ent
New Initiatives for Sustainable Agriculture Development Strategy – Making Vision a Reality
Seed Bowl:
• Seed is a critical determinant in increasing the agricultural productivity.
• The performance and efficiency of other inputs depends on the quality of seed produced and supplied.
• Telangana Government is developing a strategy to make the State, as the “Seed Bowl” of the country.
• Endowed as it is with congenial climatic conditions and soils suitable for quality seed production of various crops viz., Paddy, Maize, Soybean Castor & Cotton.
• Five year plan has been prepared for production of breeder and certified seed by involving the technical expertise of Prof. Jayashankar. Telangana State Agriculture University (PJTSAU).
• The seed production programme is planned to be taken up through Seed Village Programme and Seed Production in State Seed Farms and Government Agencies like Telanagana State Seed Development Corporation (TSSDC), Oil fed, MARKFED and HACA.
• The state produces 37.42 lakh quintals of seeds of various crops with an area of 3.22 lakh acres, mainly Hybrid paddy, Maize, Cotton and Bengal gram etc. which are supplied to our farmers and also to various other states. Thus the Telangana is the seed capital of the country.
• Production and supply of quality seed to the farmers is proposed under the plan budget for which an amount of Rs 50.00 crores is allocated to strengthen the seed chain, which includes improving of seed varietal replacement in all crops, construction of additional seed storage godowns, procurement of seed processing equipment, strengthening of seed testing laboratories etc.
• There are 10 seed farms in the state with an area of 536 ha of cultivable area.
• The main objective is to produce foundation seed and supply under the Seed Village Scheme.
• It is proposed to strengthen these farms by supplying Breeder seed for multiplication while providing assured irrigation and infrastructure support like seed processing and storage.
* Stay tuned for Crop Colonies, Agriculture Mechanization and Crop Insurance Scheme
G.Rajendra Kumar

Next Story
More Stories
ADVERTISEMENT
© 2024 Hyderabad Media House Limited/The Hans India. All rights reserved. Powered by hocalwire.com







